The process by which sheet metal is formed into usable sheet metal parts and products is called sheet metal fabrication. Sheet metal fabrication services feature a variety of fabrication processes, such as bending, drawing, flanging, punching, shearing, spinning, and stretching. All sheet metal fabrication processes seek to create high quality, long-lasting parts and products, while reducing material and labor costs. Read More…
Maysteel provides complex sheet metal fabrication with a focus on design for manufacturing. Founded in 1936, we combine our extensive engineering experience and market knowledge with an expanding supply chain footprint, allowing us to fabricate products that others can’t. We design, engineer and manufacture custom OEM sheet metal enclosures, kiosks, cabinets and racks. We have locations in the...
At Buhrt Engineering Inc., we take pride in our expertise in roll forming and sheet metal fabrication. Our team of skilled engineers and technicians is dedicated to delivering high-quality, precision-formed metal components tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients. We utilize advanced roll forming techniques to create complex, continuous profiles with exceptional accuracy, ensuring...

Accurate Metal Fabricating has been providing metal fabrication to OEM's and job shops for over 80 years. We fabricate, engineer, and perforate to the most precise specifications for the most demanding companies. We offer a full range of metal customization and fabrication capabilities that bring your design to reality. Our abilities range from forming and laser-cutting to powder coating and...

At Axis Fabrication & Machine Co., we specialize in precision sheet metal fabrication and laser cutting, delivering high-quality solutions tailored to meet the needs of diverse industries. With a commitment to craftsmanship and innovation, we provide comprehensive fabrication services that encompass cutting, forming, welding, and finishing, ensuring each component meets exact specifications.

Since 1981, American Industrial has been on the cutting edge of all things sheet metal. This has helped us achieve our spot as a leader of the industry.
More Sheet Metal Fabrication Companies
Sheet metal refers to thin, broad sheets of metal used primarily as a raw material in manufacturing. Far more than just a simple building block, sheet metal is the backbone of modern industry, serving as a foundational component across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, construction, communications, computing, electronics, food processing and storage, HVAC, military, medical device manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. If you are researching sheet metal fabrication services or comparing sheet metal fabrication companies for your next project, understanding its applications, materials, and processes will help you make the most informed decision for your specific needs.
Trusted precision sheet metal fabrication service providers offer the capability to produce an exceptionally diverse range of custom parts and products. Examples include metal furniture such as stainless steel storage units and cabinets, stairwell railings, fencing, HVAC ductwork and grating, lighting hoods, scissors, enclosures for electronics, structural elements such as bridge skeletons and aircraft frameworks, appliance housings, machine guards, equipment panels, and even intricate items like silverware and kitchen utensils. Whether you require a small batch of prototypes or high-volume production runs, modern sheet metal fabrication companies are equipped to meet demanding project specifications across commercial, industrial, and consumer use cases.
History of Sheet Metal Fabrication
The history of sheet metal fabrication is a testament to human ingenuity and the evolution of manufacturing technologies. Humans have been manipulating metal since the discovery of copper thousands of years ago. The oldest known fabricated metal artifact is a pendant found in northern Iraq, dating back to around 8700 BC. Nearly as ancient are the handheld copper hammers discovered in the Great Lakes region, particularly in present-day Michigan. People crafted these hammers between 5000 BC and 4000 BC using heat from fire. During the eras of the ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans, artisans developed and refined essential metalworking techniques. They mastered stamping, engraving, bending, and cutting, which greatly advanced the field of metal manipulation.
Leonardo da Vinci was the first to envision sheet metal fabrication in 1485, illustrating a concept for a rolling mill. The earliest operational rolling mill, established in 1501, did not match the sophistication of da Vinci’s design. These initial mills served various functions, such as creating gold sheets for coinage and slicing metal into strips. It wasn’t until 1590 that a mill closely resembling da Vinci’s vision was constructed. This mill utilized a machine that compressed metal between two rollers, allowing for more accurate sheet metal processing.
In 1615, investors established the first factory for lead and tin plate production. England introduced its first cold roll mill in 1682. The Industrial Revolution, which began around 1760, brought new machinery and products, expanding sheet metal fabrication. Inventors responded by developing new equipment, including press brakes. In 1770, Joseph Bramah, the renowned inventor and locksmith, designed the hydraulic press, significantly improving precision in metalworking. Engineers also introduced the assembly line process, which streamlined sheet metal fabrication and laid the groundwork for modern mass production.
The 1800s saw significant advancements in the metal fabrication industry with the discovery and use of aluminum. By the mid-19th century, the production of steel sheets increased markedly, thanks to Henry Bessemer’s groundbreaking method for converting iron into steel. Advancements in technology have since transformed custom sheet metal fabrication, enhancing both precision and efficiency. Automated lines equipped with robotic machinery and CNC technology now ensure greater accuracy and consistency in metalworking. Today, custom sheet metal fabrication offers virtually limitless possibilities for industries demanding both high quality and cost-efficiency.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Materials
Choosing the right sheet metal material is a critical factor in any fabrication project. Stainless steel and aluminum are the most commonly used metals for precision sheet metal work. Stainless steel is prized for its strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning, making it ideal for harsh environments and industries such as manufacturing, food processing, chemical storage, and architecture. Aluminum, known for its compressive and tensile strength as well as its light weight, is widely used in aerospace, automotive, transportation, packaging, construction, food and beverage, music, household, and electronics industries. Additionally, sheet metal can be crafted from brass, copper, nickel, titanium, and, for specialized uses, gold, silver, and platinum.
Each material exhibits unique characteristics that influence its suitability for a given application. For example:
- Stainless steel sheet metal is ideal for medical device fabrication, kitchen equipment, and marine applications due to its anti-corrosive properties.
- Aluminum sheet metal is favored for aerospace parts, electronic enclosures, and automotive body panels because of its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and machinability.
- Brass and copper sheets offer superior electrical conductivity and are frequently used in electrical components, decorative architectural elements, and precision instruments.
- Titanium and nickel alloys stand out for their high heat resistance and strength, making them suitable for aircraft components, chemical processing equipment, and high-performance automotive parts.
Are you wondering which sheet metal material is best for your specific application? Consider the operational environment, expected stresses, budget, and regulatory standards in your industry. Consult with experienced sheet metal fabricators to ensure optimal material selection for your custom components.
Sheet Metal Service Details
Sheet metal forming is a critical preliminary stage in the production of various metal parts and products. Initially, raw metal is heated until it becomes malleable. This heated metal is then shaped into long, molten slabs. These slabs are subsequently passed through large, powerful rollers, which compress them into thin, broad sheets. This process ensures the metal reaches the desired rectangular sheet form, ready for further use. Once the sheet metal is formed, it is cut to specific sizes and prepared for transportation to another manufacturing facility. At this next location, the sheets undergo design and fabrication processes.
During the part design phase, manufacturers focus on creating a detailed plan for the final product. This involves identifying potential stress points, weak areas, and other vulnerabilities that the product may encounter. A comprehensive strategy is developed and implemented to address these issues, ensuring the durability and reliability of the finished product. With the adoption of CAD (computer-aided design) and CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) tools, today’s metal fabricators can simulate stresses, optimize designs for manufacturability, and speed up the prototyping process.
Part fabrication entails shaping metal sheets to achieve the intended product. This stage involves various metalworking techniques, including machining, cutting, sawing, shearing, drilling, perforating, stretching, rolling, bending, spinning, ironing, stamping, sanding, deburring, blanking, and welding. Techniques such as spot welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, and stick welding are employed depending on the specific requirements of the fabrication process. These methods are essential for achieving precise tolerances and strong, aesthetically pleasing joints.
Heat treatment is an optional yet common step in metalworking. This process modifies the metal’s properties, either by hardening and strengthening it or by softening it for further manipulation. Methods such as tempering, quenching, and annealing are commonly used to achieve the desired material characteristics. In the assembly phase, if a precision sheet metal product consists of multiple components, these parts are assembled before the product is dispatched. This ensures that the final product is complete and operational, meeting the necessary specifications for its intended application.
Looking to learn more about custom sheet metal fabrication processes or wondering how fabrication methods affect your project cost and timeline? Explore our directory of sheet metal fabrication companies or reach out to expert fabricators for a quote and consultation.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Design
When manufacturers embark on the fabrication of custom metal parts, they meticulously consider a range of specifications. The intended purpose of the product, its required strength, the quantity needed, and adherence to industry standards all play pivotal roles in the decision-making process. Additionally, the material characteristics, such as corrosion resistance, impact resistance, and heat resistance, are critical factors that ensure the final product meets the desired performance and longevity.
Sheet metal fabricators possess the capability to craft an extensive array of custom sheet metal components. Their expertise allows them to tailor products to various shapes, sizes, complexities, and materials, thereby accommodating diverse and specific requirements. For those seeking to understand more about the intricacies of custom fabrication, engaging in discussions with potential suppliers is highly recommended. These conversations can provide valuable insights and guidance, helping to ensure that the final product aligns perfectly with the project’s needs and expectations.
Sheet Metal Machinery & Processes
Sheet metal fabricators
Sheet metal fabricators employ a blend of manual expertise and advanced technology, often utilizing computer-operated (CNC) machines to achieve precision and efficiency. Their workshops are equipped with an extensive array of machinery, enabling them to execute complex fabrication tasks. Among the essential equipment are CNC-controlled punch and die machines, automated production lines, and press brakes. Additionally, they utilize various tools, including drills and laser cutters, ensuring they can meet diverse fabrication needs with accuracy and skill.
Punch and die machines
Punch and die machines are essential tools in the manufacturing industry for shaping products from sheet metal. The process begins with securing one or more flat metal sheets on a designated surface. Once the workpiece is positioned, the punch mechanism is activated, driving the punch downward to shape the metal sheet. The force of the punch deforms the metal, imprinting it with the precise shape of the punch.
Alternatively, manufacturers can utilize a die to achieve the desired form. In this method, metal sheets are placed over a die, and a press brake is employed to press the metal into the die, resulting in the metal conforming to the die’s shape. This process allows for the creation of intricate and precise metal components, making punch and die machines invaluable in various manufacturing applications.
Automated lines
Automated lines, utilizing robotic workers in place of humans, represent a significant advancement in assembly line technology. These systems are designed for maximum efficiency, significantly reducing the likelihood of errors that can occur with manual labor.
Their precision and reliability make automated lines particularly prevalent in large-scale manufacturing facilities, where they streamline production processes and enhance overall productivity. The implementation of robotic workers in these automated lines not only ensures consistent quality but also allows factories to operate at a higher capacity with fewer interruptions. This makes them a cornerstone of modern lean manufacturing practices and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Press brakes
Press brakes are essential machines in the metalworking industry, designed to precisely bend sheet metal to desired specifications. These versatile tools are often used in combination with other specialized equipment, such as shaped dies and punches, to achieve intricate and accurate bends. By integrating press brakes with these complementary devices, metalworkers can enhance the efficiency and precision of their operations, producing high-quality components for various applications. Press brakes are especially critical for creating components for architectural panels, HVAC ductwork, and custom enclosures.
Drills
Drills are indispensable cutting tools utilized by manufacturers to create precise holes in various materials. These tools feature rotating tips, which enable them to efficiently penetrate surfaces and achieve clean, accurate cuts. The ability of drills to consistently produce well-defined holes makes them a fundamental component in a wide range of manufacturing processes, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the final products.
Laser cutting tools
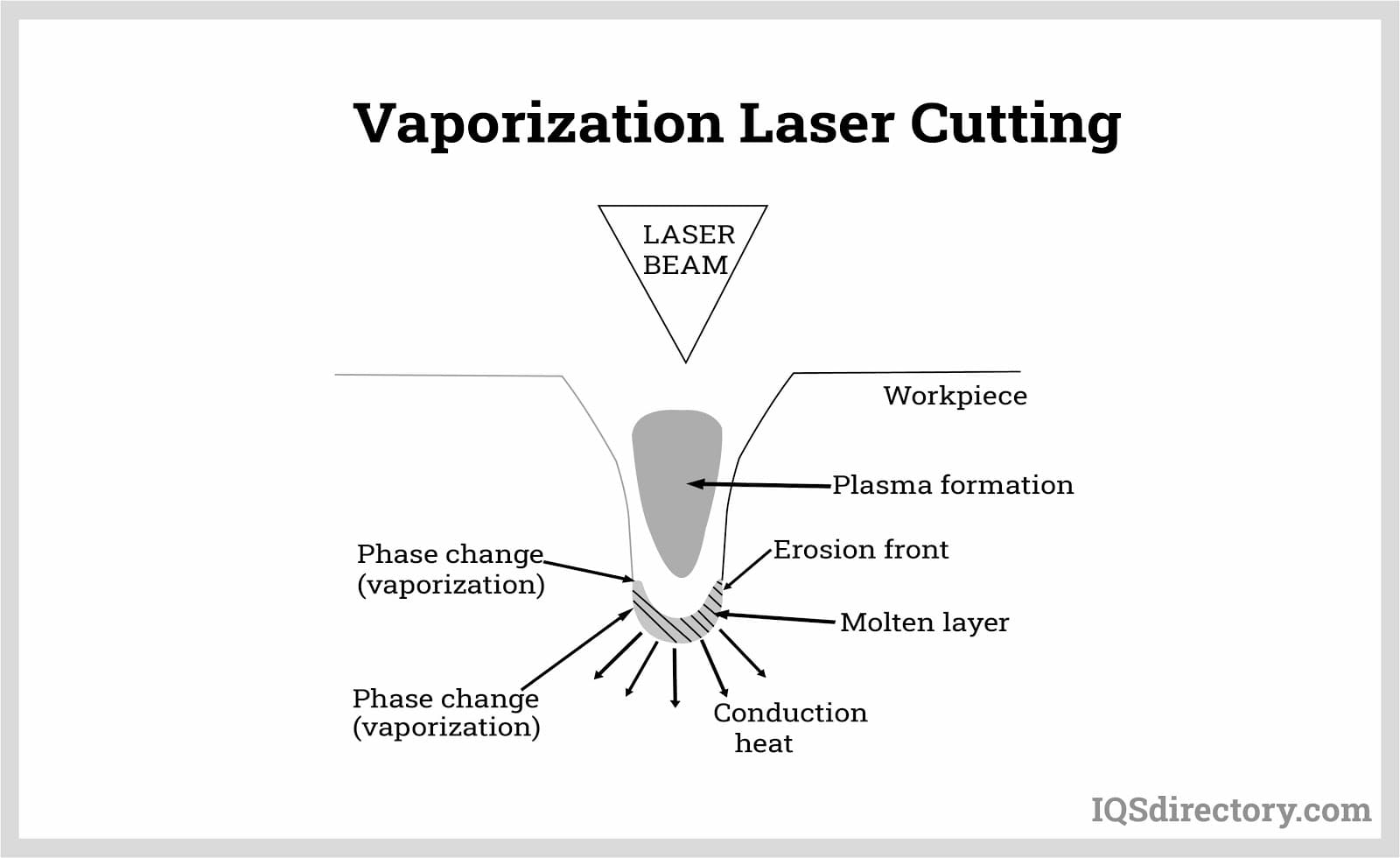
Laser cutting tools employ precision laser beams to achieve exceptionally clean and high-quality cuts. This advanced technology allows for intricate designs and precise edges, ensuring a superior finish on various materials. The laser’s accuracy not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the cut but also minimizes material wastage, making it a preferred choice in industries where precision and efficiency are paramount. Laser cutting is particularly valuable for prototyping, custom signage, electronic housings, and decorative architectural features.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Processes
Key processes in sheet metal fabrication and machining, whether conducted through CNC or manual methods, include bending, drawing, flanging, stretching, punching, shearing, and spinning. These essential techniques are integral to crafting and molding metal parts to exacting standards and specifications. If you’re evaluating which fabrication process is best for your product, consider how each step impacts overall quality, speed to market, and cost-effectiveness.
Bending
Bending is generally performed using a standard die set, which allows for the creation of various common shapes such as C-shapes, V-shapes, and channel shapes. This process involves a bending machine that applies force to deform the metal along a predetermined straight line, ensuring precise and consistent results. Through this method, the metal is expertly manipulated to achieve the desired form, maintaining structural integrity and meeting specific design requirements.
Drawing
Drawing and deep drawing are advanced stamping techniques that skillfully transform flat sheet metal into diverse three-dimensional configurations. These processes are crucial in the manufacturing sector, allowing the formation of complex shapes with meticulous accuracy. Through these methods, flat metal sheets are molded into intricately designed, high-quality components, meeting the specific demands of various industries. The adaptability and precision of drawing and deep drawing make them indispensable for producing reliable and finely crafted parts across a broad spectrum of applications, from automotive engineering to consumer electronics.
Flanging
Flanging is a specialized stamping process integral to many manufacturing operations. This technique involves bending a material along a precisely defined curved line. By employing flanging, manufacturers can achieve complex shapes and enhance the structural integrity of the material, making it a crucial step in producing high-quality, durable components.
Stretching
Stretching represents an integral stamping process in the manufacturing industry. This technique entails securing flat sheet metal firmly by its edges and subsequently extending it to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. Through this method, manufacturers are able to produce smoothly contoured auto body parts, showcasing both precision and uniformity. This process is essential for creating components that meet exacting standards of quality and performance in automotive manufacturing.
Punching
Punching involves the precise piercing of sheet metal. This process begins with positioning the metal between a punch and a die, both of which are securely mounted within a press. As the press exerts significant force, the punch drives into the die, effectively creating a hole in the metal. In certain applications, the punch and die are designed to “nest” together, forming a depression in the metal rather than a complete hole. It is important to distinguish punching from perforating, the latter being a method that produces multiple small holes across a flat surface.
Shearing
Shearing is a precision cutting technique that employs large shears to accurately slice through sheet metal. Following this, the spinning process involves the use of rigid tools or rollers to secure a heated sheet against a rotating form, known as a mandrel. As the mandrel rotates, the sheet metal is gradually stretched and shaped into a tubular component. This method is frequently utilized by manufacturers to produce a variety of specialized items, including satellite dishes, metal kitchen funnels, rocket motor casings, and missile nose cones.
Other sheet metal fabrication and machining processes include wheeling, water jet cutting, rolling, roll forming, press brake forming, photochemical machining, laser cutting, ironing, incremental sheet forming, hemming and sealing, hydroforming, expanding, curling, and decambering. Each process plays a vital role in delivering the required geometries, tolerances, and surface finishes for a wide range of end-use applications.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is essential to a vast array of industries and applications. Common uses include:
- Automotive manufacturing: Body panels, chassis parts, brackets, and engine components
- Aerospace and defense: Aircraft skins, structural frames, missile housings, and satellite components
- Construction: Roofing, wall panels, ductwork, structural beams, and staircases
- HVAC: Duct systems, registers, diffusers, and air handlers
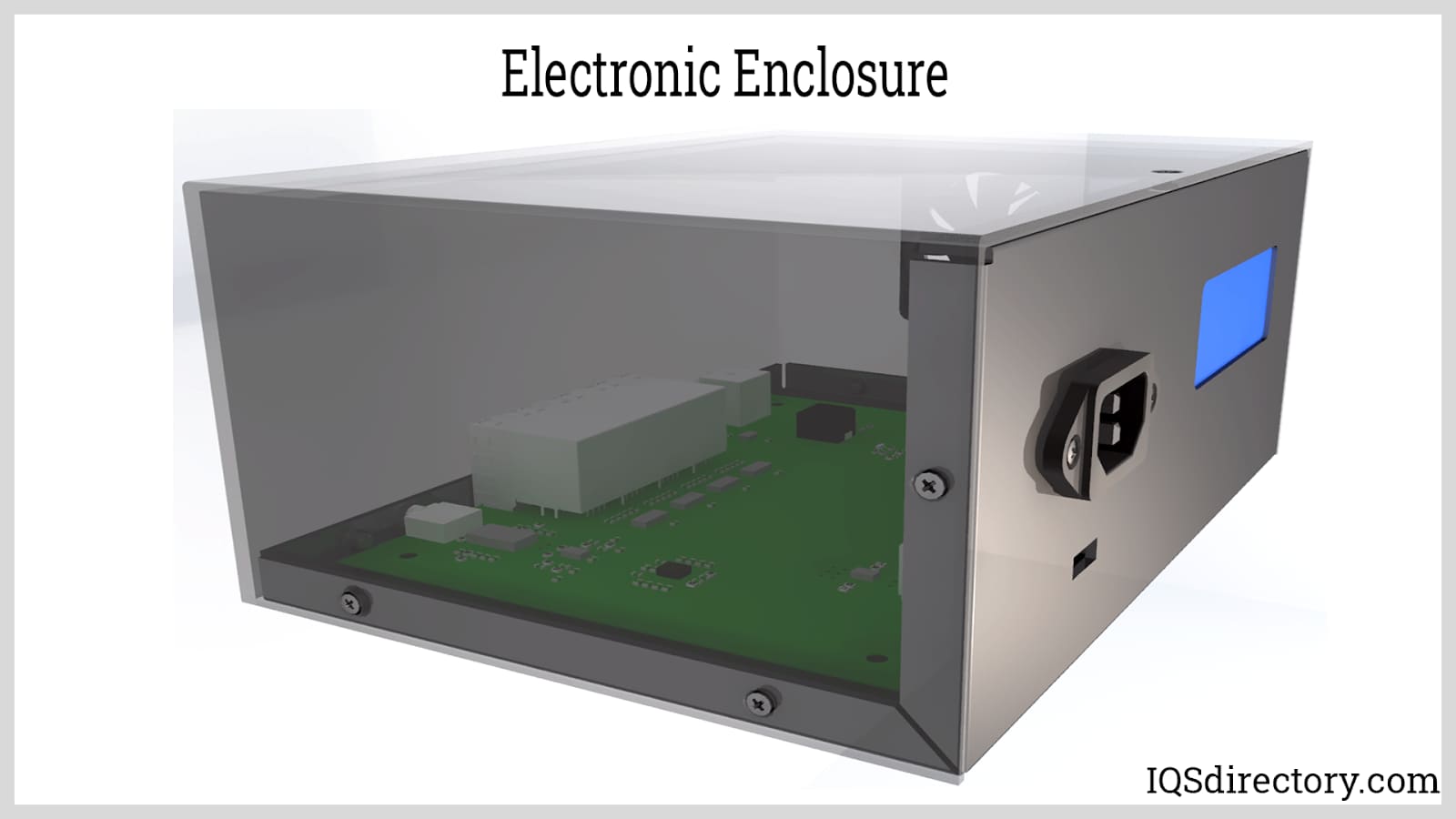
- Electronics: Enclosures, racks, mounting panels, and heatsinks
- Medical devices: Equipment housings, sterile containers, and surgical instrument trays
- Food processing: Conveyors, hoppers, mixers, and stainless steel work surfaces
- Renewable energy: Solar panel frames, wind turbine housings, and battery enclosures
- Consumer products: Appliances, furniture, lighting fixtures, and decorative hardware
Are you looking for a sheet metal fabrication supplier with expertise in your industry? Browse our comprehensive company listings to compare specialized providers by industry focus, certifications, and capabilities.
Benefits of Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication
Custom sheet metal fabrication delivers a host of advantages for manufacturers, engineers, and product designers:
- Design Flexibility: Create virtually any shape or configuration, from simple brackets to complex assemblies.
- Material Variety: Select from a broad range of metals and alloys to match application requirements.
- Precision and Consistency: Advanced CNC and automated processes ensure tight tolerances and repeatability.
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly move from design to prototype and iterate faster.
- Durability: Metal components withstand extreme conditions and offer long service life.
- Cost Efficiency: Scalable production methods support both small runs and high-volume manufacturing.
- Integration: Combine with other manufacturing processes such as welding, assembly, powder coating, or finishing for turnkey solutions.
Want to know how custom sheet metal fabrication can improve your products or manufacturing process? Contact expert fabricators for a free consultation and project review.
How to Choose a Sheet Metal Fabrication Supplier
Choosing the right sheet metal fabrication supplier is critical for achieving project success. Here are key decision factors to consider:
- Experience and Reputation: Does the company have a proven track record in your industry or for your specific application?
- Capabilities: Are they equipped for prototyping, large-scale production, tight tolerances, or specialized processes such as laser cutting or powder coating?
- Certifications: Do they hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, AS9100, or industry-specific quality standards?
- Material Sourcing: Can they source and process the metals you require?
- Design Support: Do they offer engineering, CAD, and prototyping support?
- Lead Times: What is their typical turnaround time for quotes, prototypes, and production?
- Quality Assurance: What inspection and quality control processes are in place?
- Cost: Are their pricing models transparent and competitive for both short and long runs?
- After-Sales Support: Do they offer installation, maintenance, or replacement parts services?
To identify the ideal supplier for your needs, explore the comprehensive list of quality sheet metal fabrication suppliers provided on this page. Before reviewing the list, clearly outline your specific requirements, including budget, timeline, quality standards, delivery preferences, and post-delivery needs such as installation assistance, parts replacement, and maintenance. Use this information to compare and assess the capabilities and services of each supplier, narrowing down your options to three or four potential candidates. Engage in detailed discussions with representatives from these suppliers, and based on these conversations, select the company that best fits your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sheet Metal Fabrication
- What is the difference between sheet metal fabrication and metal stamping?
Sheet metal fabrication refers to a range of processes used to manipulate, cut, and assemble metal sheets into finished components. Metal stamping is a specific process within fabrication where a press is used to shape or cut metal using dies. - How do I choose the right sheet metal thickness for my project?
Factors include structural requirements, intended use, weight constraints, and cost. Consult with your fabricator and reference industry standards for guidance. - Can I get custom prototypes before committing to full production?
Yes, most modern sheet metal fabrication shops offer rapid prototyping and small-batch runs to validate designs before scaling up. - What finishing options are available for fabricated sheet metal parts?
Common finishes include powder coating, painting, anodizing, plating, polishing, and passivation. Each offers different levels of corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetics. - Which industries rely most on sheet metal fabrication?
Key industries include automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, food processing, medical devices, HVAC, and renewable energy.
Still have questions about sheet metal fabrication services, processes, or suppliers? Contact our team or explore our resources for additional guidance.
Explore More: Sheet Metal Fabrication Resources
- View all sheet metal fabrication companies
- Compare sheet metal fabricators
- Request a custom sheet metal fabrication quote





 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals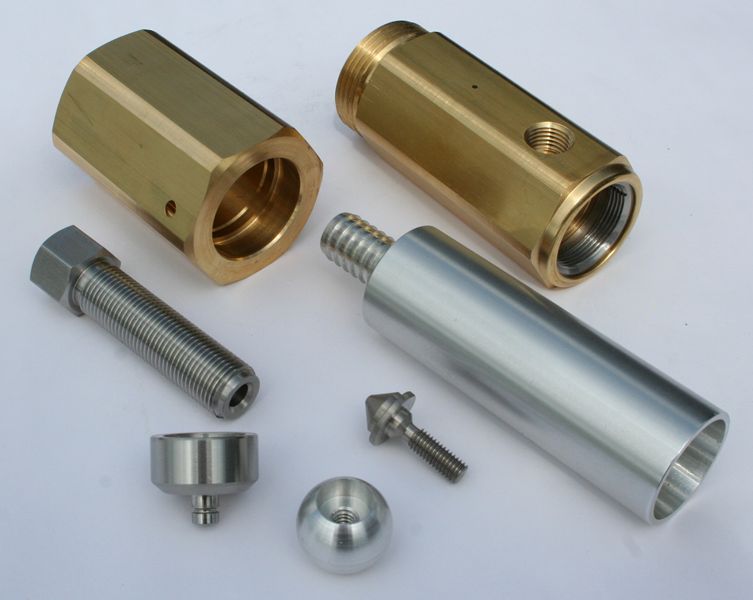 Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services